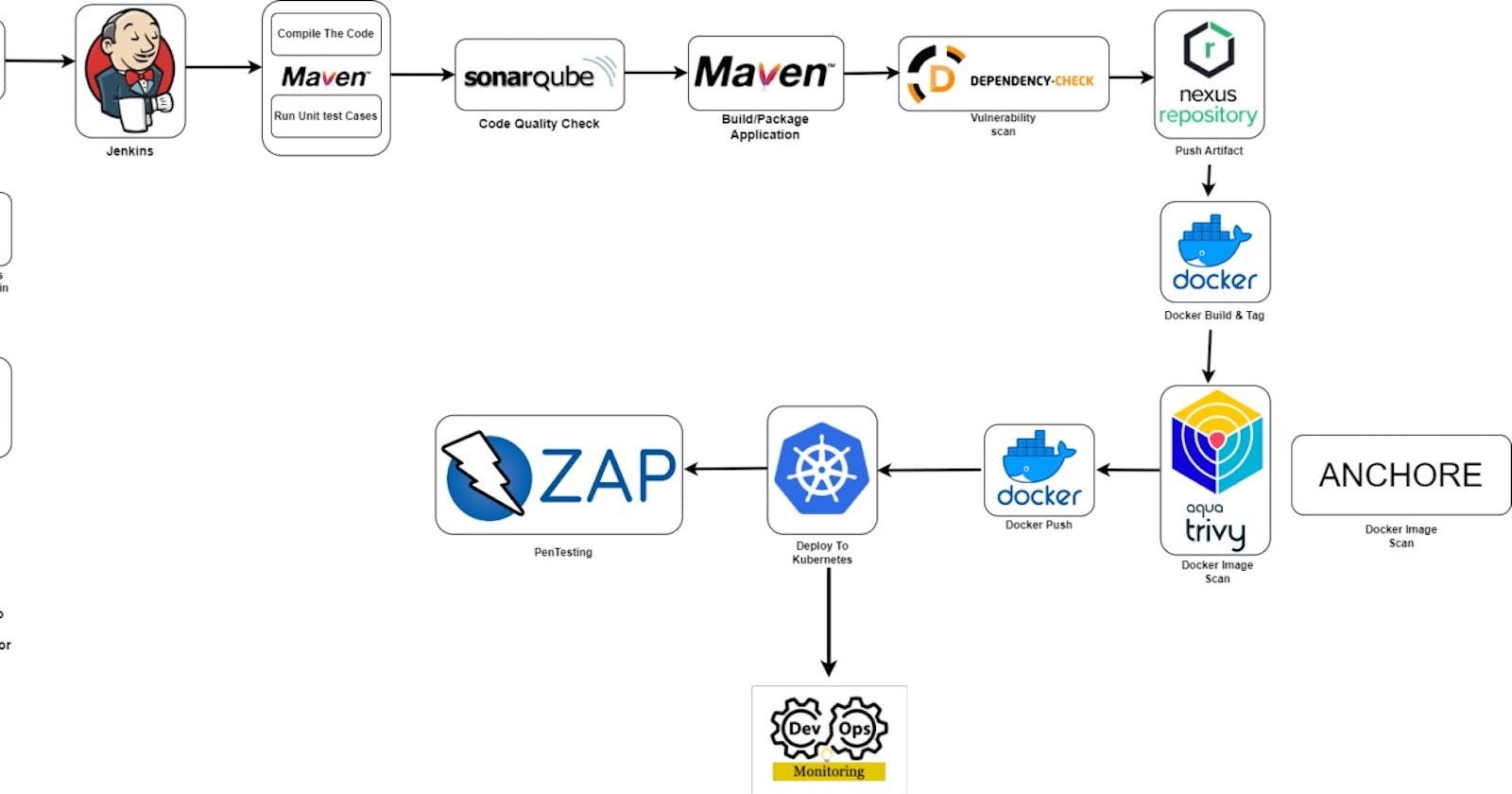
Comprehensive pipeline ensures that code changes go through various stages of testing and analysis before being deployed, reducing the likelihood of issues in production. Let's summarize the key steps in this pipeline:
Jira Ticket Assigned:
- Developer receives a Jira ticket outlining the task or feature to be implemented.
Code Pushed to GitHub Feature Branch:
- Developer creates a feature branch and pushes code changes related to the Jira ticket.
Jenkins Job:
Jenkins, triggered by a webhook or scheduled job, monitors the repository for changes.
Upon detecting a new commit in the feature branch, Jenkins triggers the CI/CD pipeline.
Maven Compile & Run Test Cases:
Jenkins checks out the code, compiles it using Maven, and runs unit and integration tests.
Test results are collected and stored for analysis.
SonarQube Analysis:
Jenkins triggers a SonarQube analysis to scan the code for quality issues, vulnerabilities, and technical debt.
Analysis results guide the development team in making improvements.
Maven Package:
- If tests and analysis are successful, Jenkins packages the application using Maven.
OWASP Dependency Check:
Jenkins uses OWASP Dependency Check to identify and report any vulnerable dependencies.
The pipeline can be halted if critical vulnerabilities are found.
Push to Nexus Repository:
- Packaged application artifacts are pushed to a Nexus repository for centralized storage.
Docker Build and Tag:
Jenkins triggers a Docker build, creating an image based on the application code and dependencies.
The Docker image is tagged with version information.
Trivy Scan Docker Image:
- Jenkins runs Trivy, a vulnerability scanner, on the Docker image to identify vulnerabilities in OS packages and application dependencies.
Docker Push Image:
- If the Trivy scan passes, Jenkins pushes the Docker image to a container registry (e.g., Docker Hub, AWS ECR).
Trivy Scan Kubernetes Cluster:
- Jenkins triggers a Trivy scan of the deployed images in the Kubernetes cluster to identify vulnerabilities.
Deploy to Kubernetes Cluster:
- If all scans and tests pass, Jenkins deploys the Docker image to the Kubernetes cluster using deployment scripts or configuration files.
OWASP Zap Penetration Testing:
- After deployment, OWASP Zap conducts automated security tests against the application to identify vulnerabilities.
Post-Deployment Monitoring and Analysis:
Continuous monitoring tools (e.g., Prometheus, Grafana) track application performance and health.
Logs and metrics are analyzed to ensure the application is running as expected.
Iterate and Improve:
- Based on monitoring data and feedback, the development team iterates and improves both the application and the CI/CD pipeline.
This pipeline integrates security measures at multiple stages, from code analysis to vulnerability scanning in both Docker images and the Kubernetes cluster. It also emphasizes continuous improvement, reflecting the DevOps principle of iterative refinement. Organizations can customize this template to align with their specific needs and technology stack.