Overview of Maven concepts, along with examples and commands to illustrate each step:
Project Creation: To create a new Maven project, you can use the
mvn archetype:generatecommand and select a suitable archetype. An archetype is a template for creating a specific type of project. For example:mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.example -DartifactId=my-project -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DinteractiveMode=falseThis command creates a new Maven project with the specified group ID (
com.example) and artifact ID (my-project) using themaven-archetype-quickstartarchetype.Project Structure: The project structure has already been explained in the previous response. Maven follows a standard directory structure for source code, resources, tests, and artifacts.
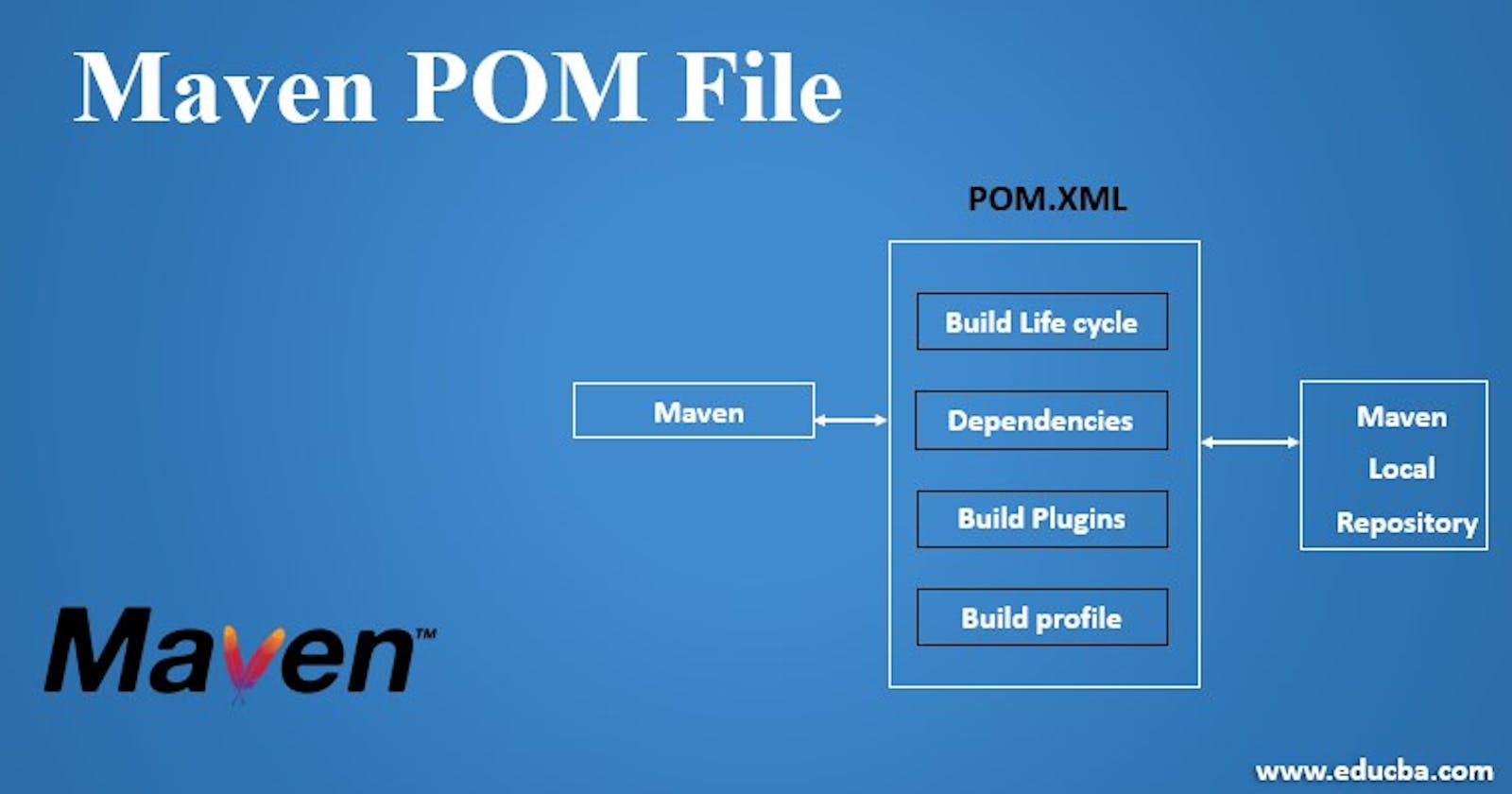
POM (Project Object Model): The POM is an XML file named
pom.xmlthat contains project configuration, dependencies, build settings, and more.Here's an example of a simple
pom.xmlfile:<project> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>my-project</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <dependencies> <!-- Define project dependencies here --> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <!-- Define build plugins here --> </plugins> </build> </project>Dependency Management: Maven makes it easy to manage project dependencies. You can add dependencies to the
<dependencies>section of yourpom.xmlfile. Maven automatically downloads the required dependencies from remote repositories.Example dependency entry in
pom.xml:<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <version>1.7.32</version> </dependency> </dependencies>Building the Project: Maven provides a set of built-in lifecycle phases for building, testing, and packaging projects. Common Maven commands include:
mvn clean: Cleans the target directory.mvn compile: Compiles the source code.mvn test: Runs tests.mvn package: Packages the compiled code (e.g., JAR, WAR).mvn install: Installs the project artifact to the local repository.mvn deploy: Deploys the project artifact to a remote repository.
Running Goals: You can also run specific Maven goals using the
mvncommand. For example:mvn clean compile mvn test mvn packageRunning Plugins: Maven plugins enhance the build process. For instance, the
maven-compiler-pluginhelps compile code, and themaven-surefire-pluginhandles test execution.Example plugin configuration in
pom.xml:<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>External Repositories: Maven downloads dependencies from remote repositories. You can configure additional repositories in your
pom.xmlfile.Example repository configuration:
<repositories> <repository> <id>central</id> <url>https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2</url> </repository> <!-- Other repositories --> </repositories>Running Custom Commands: You can run custom Maven plugins or commands using the
mvncommand, referencing the plugin's goal.For example, if you have a custom plugin named
my-pluginwith a goal namedcustom-goal, you can run it like this:mvn my-plugin:custom-goal